


| libageo · Ebene · Richtungsfunktionen |
| » | vector | plane. | direction | (point) | ||
| vector | plane. | direction | (line) | |||
| vector | plane. | direction | (plane) | |||
| vector | plane. | direction | (circle) | |||
| vector | plane. | direction | (cylinder) | |||
| vector | plane. | direction | (sphere) | |||
| vector | direction | (plane, point) | ||||
| vector | direction | (plane, line) | ||||
| vector | direction | (plane, plane) | ||||
| vector | direction | (plane, circle) | ||||
| vector | direction | (plane, cylinder) | ||||
| vector | direction | (plane, sphere) |
| Die Methode, respektive Funktion, direction liefert einen normierten Richtungsvektor von einer Ebene zu einem anderen Geometrieelement. | |
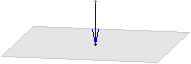
| Richtung Ebene-Punkt | |
| Die Richtungsvektor steht lotrecht auf der Ebene und zeigt von dieser zum Punkt. | |

|
|
| Richtung Punkt-Ebene | |
| Die Richtungsvektor steht lotrecht zur Ebene und zeigt auf diese. | |

|
|
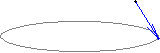
| Richtung Punkt-Kreis | |
| Die Richtungsvektor steht lotrecht zum Kreis. Für Punkte in der Kreisebene, die außerhalb des Kreises liegen, zeigt er zum Kreismittelpunkt, für Punkte in der Kreisebene innerhalb des Kreises vom Kreismittelpunkt weg. | |

|
|
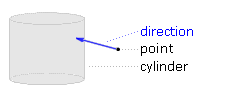
| Richtung Punkt-Zylinder | |
| Die Richtungsvektor steht lotrecht zum Zylindermantel (und der Zylinderachse). Er zeigt in jedem Fall zum Zylindermantel. Für Punkte außerhalb des Zylinders zeigt er zur Zylinderachse, für Punkte innerhalb weg von der Zylinderachse. | |

|
|
| Richtung Punkt-Kugel | |
| Die Richtungsvektor steht lotrecht zum Kugelmantel. Für Punkte außerhalb der Kugel zeigt er zum Kugelmittelpunkt, für Punkte innerhalb weg vom Kugelmittelpunkt. | |

|
|
point p(10,20,30); point q(0,0,0); vector v = p.direction(q); |
// v=vector(-0.267,-0.535,-0.802) |
||
|
point p(10,20,30); line ln( point(0,0,0), vector(1,0,0) ); vector v = p.direction(ln); |
// v=vector(0.162,-0.162,-0.973) |
||
|
point p(10,20,30); plane pl( point(0,0,0), vector(0,0,-1) ); vector v = p.direction(pl); |
// v=vector(0.000,0.000,-1.000) |
||
|
point p(5,5,5); circle cr( point(0,0,0), vector(0,0,1), 10 ); vector v = p.direction(cr); |
// v=vector(0.357,0.357,-0.863) |
||
|
point p(5,5,5); cylinder cr( point(0,0,0), vector(0,0,1), 10 ); vector v = p.direction(cc); |
// v=vector(0.707,0.707,0.000) |
||
|
point p(5,5,5); sphere cr( point(0,0,0), 10 ); vector v = p.direction(sp); |
// v=vector(0.577,0.577,0.577) |
| Punkt: Abstandsfunktionen, Übersicht, Alle Methoden und Operatoren; Gerade, Ebene, Kreis, Zylinder, Kugel; Stichwortverzeichnis |
